- Home
- Blog
- Cloud Services
- What is Cloud Computing? How Should Businesses Choose?
What is Cloud Computing? How Should Businesses Choose?

With the advent of the digital era, cloud technology has become one of the core infrastructures for many businesses. Whether for large enterprises or SMEs, companies are increasingly relying on cloud services to enhance work efficiency while ensuring secure and convenient access to their data.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that allows access to servers via the internet, enabling users to run software and manage data on these servers. These cloud servers are housed in data centers located around the world, eliminating the need for users and businesses to manage physical servers or install applications themselves.
In simple terms, the cloud functions like a “virtual hard drive” on the internet, allowing users to access data and run applications anytime, without being constrained by physical devices. This flexibility enables businesses to focus on their core operations while reducing their dependency on and burden of managing technical infrastructure.
Different Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services can be categorized into several main types depending on specific requirements:
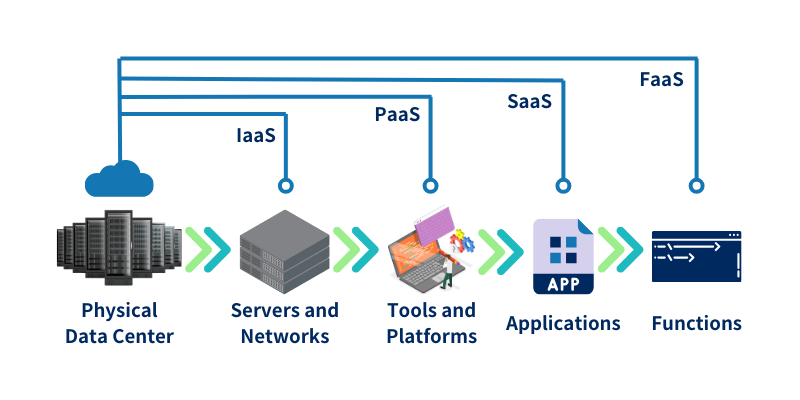
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS allows businesses to rent fundamental hardware resources—such as servers, storage, and networks—through cloud service providers. With IaaS, companies don’t need to purchase or maintain physical hardware. Instead, they can configure and use resources as needed, providing scalability and cost-efficiency.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a complete set of tools and platforms for developing, running, and managing applications. Businesses can focus on innovation and application development without the need to set up or manage the underlying environment, making the process more streamlined and efficient.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications that businesses can access directly without installation or maintenance. This type of service helps companies save on the costs of software installation, updates, and ongoing maintenance, providing a convenient and user-friendly solution.
Serverless - Functions as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS is a modern form of cloud service where developers simply write and deploy application code, and the cloud provider automatically allocates computing resources based on actual needs. This eliminates the need for managing server infrastructure, offering unparalleled flexibility and scalability.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cloud Service Deployment Models: Public, Private, and Hybrid
The deployment model of cloud services determines how they are managed and accessed.
Public Cloud
Public clouds are cloud infrastructures operated and managed by third-party cloud service providers and are available for use by any business or individual. All hardware resources, networks, and applications are shared over the internet. The main advantages of public clouds are their low cost and scalability, but they offer less control over security.
Private Cloud
Private clouds are dedicated cloud infrastructures set up for a single business or organization, usually managed internally or by a third-party provider. Since all resources are exclusive to one organization, private clouds offer greater security and control, making them suitable for businesses with high-security requirements.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds combine public and private cloud deployment models, allowing businesses to switch between the two based on their needs. This approach enables organizations to protect sensitive data while leveraging the flexibility of public clouds. However, managing a hybrid cloud can be more complex.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cloud Services: Beneficial for Businesses of All Sizes
Cloud services are not only suitable for large enterprises but also offer significant advantages for SMBs and startups. Below are some scenarios where adopting cloud services can be highly beneficial:
Businesses Requiring Flexible Resources
When a business experiences fluctuating demands, cloud services provide resources that can scale flexibly based on needs, avoiding excessive capital expenditures.
Distributed Teams
For companies with employees located in different regions, cloud services offer tools for remote access and collaboration anytime, anywhere, significantly improving work efficiency.
Businesses Looking to Reduce IT Costs
Cloud services help reduce expenses on hardware, software, and maintenance, making them ideal for small and medium-sized businesses aiming to lower IT infrastructure costs.
Businesses Needing Powerful Data Processing Capabilities
Cloud services provide high-performance computing resources, making them suitable for businesses requiring extensive data analysis and processing, such as those in the financial industry or e-commerce platforms.
Tailored Solutions for Your Digital Transformation
In the journey of digital transformation, businesses need more than just technology—they require a customized, integrated solution. Here’s what we offer:
- Integrated Cloud and On-Premise Solutions: Seamlessly combine cloud and on-premise infrastructures to meet your business needs.
- Secure Sensitive Data: Ensure data security while complying with regulatory requirements.
- Cost Reduction with Enhanced Agility: Lower operational costs while improving business flexibility and stability.
- 24/7 Technical Support and Recovery: Reliable support and robust recovery capabilities to keep your business running smoothly.
Whether you’re a business seeking digital transformation or an organization aiming to optimize your existing IT infrastructure, Core Winner provides integrated solutions that combine cloud and on-premise technologies. We help you safeguard your data while enjoying the flexibility and efficiency that cloud technology brings.
(1).png)
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- Enterprise Cybersecurity Strategy: Zero Trust, Cyber Resilience, and AI Defense
- IoT and Smart Cities: Building a Smarter, More Sustainable Future
- Cloud Gaming Market Boom: The New Battleground for the Gaming Industry
- The Convergence of AI and Cloud Technologies: Dual Engines Driving the Future Technology
- Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Common Threats and Defense Strategies


.png)

