- Home
- Blog
- Cloud Services
- Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Common Threats and Defense Strategies
Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Common Threats and Defense Strategies

In today's digital age, information security has become an indispensable issue for both businesses and individuals. Whether it's protecting personal privacy, safeguarding corporate secrets, or ensuring the stable operation of systems, achieving a secure environment requires adherence to three critical elements—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (the CIA triad). This article explains common security threats and effective countermeasures in an easy-to-understand way, helping you protect every piece of valuable data in our increasingly challenging digital landscape.
The CIA Triad of Information Security
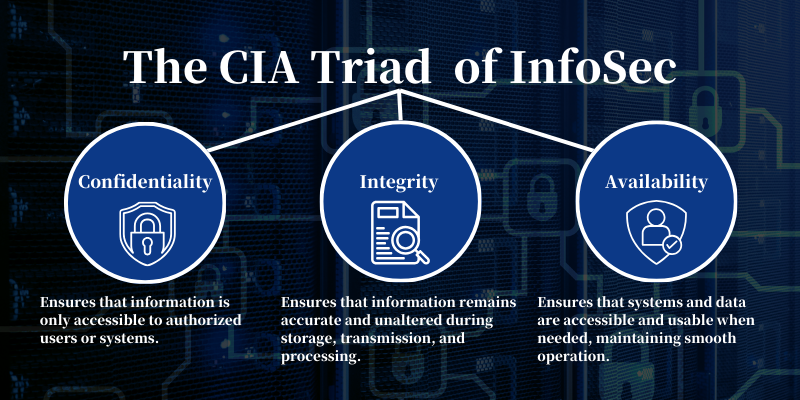
1. Confidentiality
- Definition: Ensuring that information is accessible only to authorized users or systems, preventing unauthorized reading or disclosure.
- Key Measures:
- Encryption: Using technologies like SSL/TLS protocols and AES encryption to protect data during transmission.
- Access Control: Implementing strict user authentication, multi-factor authentication, and fine-grained access controls so that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
2. Integrity
- Definition: Maintaining the accuracy and consistency of information during storage, transmission, and processing, preventing unauthorized modifications or damage.
- Key Measures:
- Digital Signatures & Hash Algorithms: Utilizing methods such as MD5 or SHA to verify that data has not been tampered with during transmission.
- Backups & Verification: Regularly backing up critical data and performing integrity checks to quickly restore accurate information if anomalies occur.
3. Availability
- Definition: Ensuring that authorized users have timely access to information and systems whenever needed.
- Key Measures:
- Redundant Systems & Fault Tolerance: Establishing backup systems and multiple failure recovery mechanisms to reduce single points of failure.
- DDoS Protection: Implementing robust measures to combat distributed denial-of-service attacks, ensuring networks and systems remain stable under heavy loads.

Common Information Security Threats
- Malware Attacks:
Viruses, worms, and Trojan horses can damage system functions, steal sensitive data, or even cause system outages.
- Phishing:
Attackers disguise themselves as trusted entities to trick users into providing account credentials, credit card details, or other sensitive information.
- DDoS Attacks:
Overwhelming a target server with excessive, often fake traffic to disrupt normal operations and compromise system availability.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:
Interceptors compromise data by intercepting and potentially altering communications between two parties, leading to data leakage or manipulation.
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities:
Exploiting undiscovered or unpatched software vulnerabilities before developers have a chance to address them.
- Password Attacks:
Utilizing brute force or guessing techniques to crack user passwords and gain unauthorized access to systems or data.
- Cloud Security Threats:
As more data and applications move to the cloud, issues like unauthorized access, data breaches, and configuration errors become increasingly critical.
- Insider Threats:
Risks arising from intentional or unintentional actions by internal personnel that can lead to data breaches or system damage.

Information Security Protection Strategies
- Education & Training:
Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices to boost awareness and mitigate risks from social engineering and other tactics.
- Strengthen Access Controls:
Use multi-factor authentication and role-based access control to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
- Regular Updates & Patching:
Promptly apply the latest security patches and software updates to close known vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of attacks.
- Data Encryption:
Encrypt sensitive information during transmission and storage to protect it from unauthorized access.
- System Monitoring & Auditing:
Continuously monitor networks and systems for abnormal activities, allowing for early detection of security breaches and rapid response.
Conclusion
The three fundamental pillars of information security—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—are essential for protecting our digital assets. In an era marked by cloud computing and exponential data growth, it is vital to understand these elements and implement robust strategies to defend against threats such as malware, phishing, DDoS attacks, cloud security vulnerabilities, and insider risks. By doing so, we can ensure the safety of our crucial data and create a stable, reliable digital environment for both businesses and individuals.
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- Enterprise Cybersecurity Strategy: Zero Trust, Cyber Resilience, and AI Defense
- IoT and Smart Cities: Building a Smarter, More Sustainable Future
- Cloud Gaming Market Boom: The New Battleground for the Gaming Industry
- The Convergence of AI and Cloud Technologies: Dual Engines Driving the Future Technology
- Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Common Threats and Defense Strategies
